Prunus laurocerasus 'Zsófi' SOFIA cherry laurel, common laurel, English laurel
Prunus
The genus Prunus is quite extensive and, above all, remarkably diverse – it includes around 350 different species, some of which you would hardly place in the same group at first glance. Its representatives occur from Asia through Europe and North Africa to North America. The genus comprises trees and shrubs valued mainly for their abundant and attractive flowering, as well as species with delicious edible fruits, and in this particular case an evergreen species whose persistent foliage becomes especially important during the dormant season, when most other woody plants are leafless. This species is known as cherry laurel (Prunus laurocerasus) and originates from regions around the Black Sea, the Caucasus, and northern Turkey, where it grows in submontane forests and on moist, shaded slopes. Its glossy, leathery leaves resemble those of true laurel, and this similarity that gave rise to its name – lauro‑cerasus, meaning “laurel cherry.” It reached Europe as early as the 16th century and, thanks to its frost hardiness, is today one of the most important evergreen woody plants even in Central European climate.
Cherry laurel was scientifically described in 1753 by Carl Linnaeus in his seminal work Species Plantarum, where it received its still accepted name Prunus laurocerasus. A later, now obsolete name, Laurocerasus officinalis, nevertheless points to a much older history of cultivation and use. A laurel‑like plant identified with cherry laurel is already mentioned by Theophrastus, Dioscorides and Pliny the Elder, who noted its unusual properties. From the leaves of cherry laurel, a distillate known as aqua laurocerasi was prepared and, when used with due caution, employed as a sedative – hence the Latin epithet officinalis, meaning medicinal. Historically and with documentary support, cherry laurel, its introduction, and its first cultivation in European gardens can be traced to the year 1576. This date fits well within the period of diplomatic missions between the Ottoman Empire and the Habsburgs, when seeds, cuttings, and young plants of previously unknown species were brought from Constantinople to Central Europe through networks associated with figures such as the imperial envoy David Ungnad (1530–1600) and the botanist Carolus Clusius (1526–1609). The transfer of newly discovered plants was regarded as a gift equal in value to gold, works of art, or archaeological finds, and represented an important expression of learning, prestige, and practical knowledge of the natural world.
SOFIA is a Hungarian cherry laurel variety from 2020 and an attractive addition to the family of new and hardy varieties from Hungarian breeders. It was granted an EU patent 53851 in 2020, and a year before it won Gold Medal at a prestigious fair of novelties Plantarium 2019.
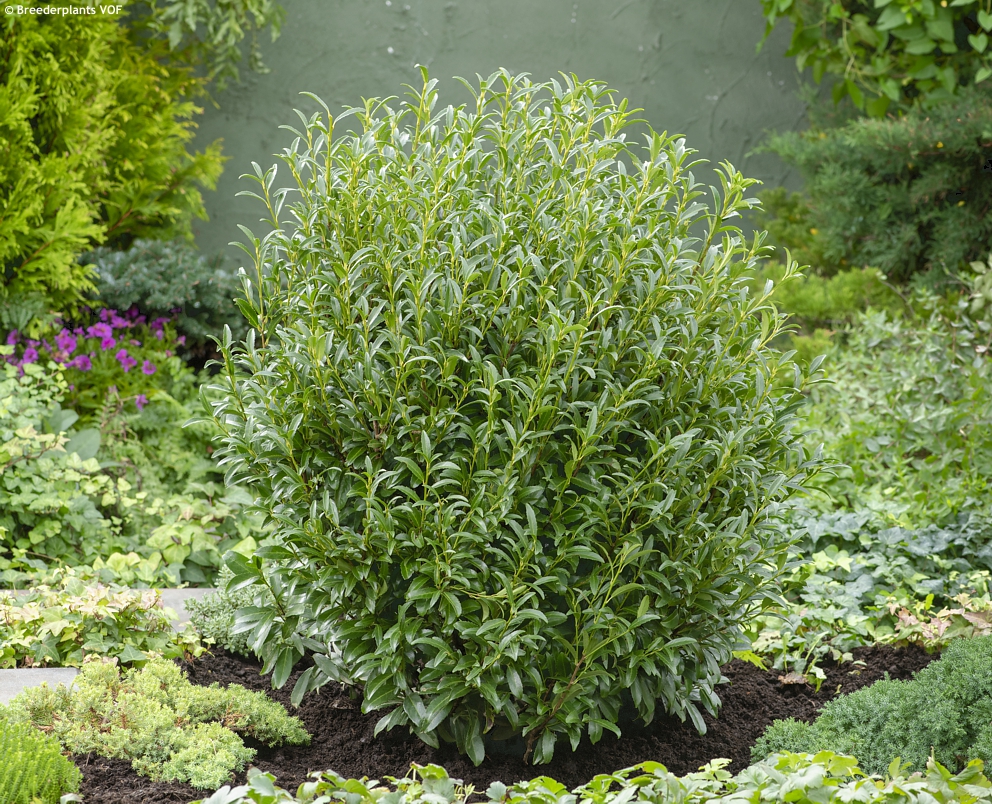
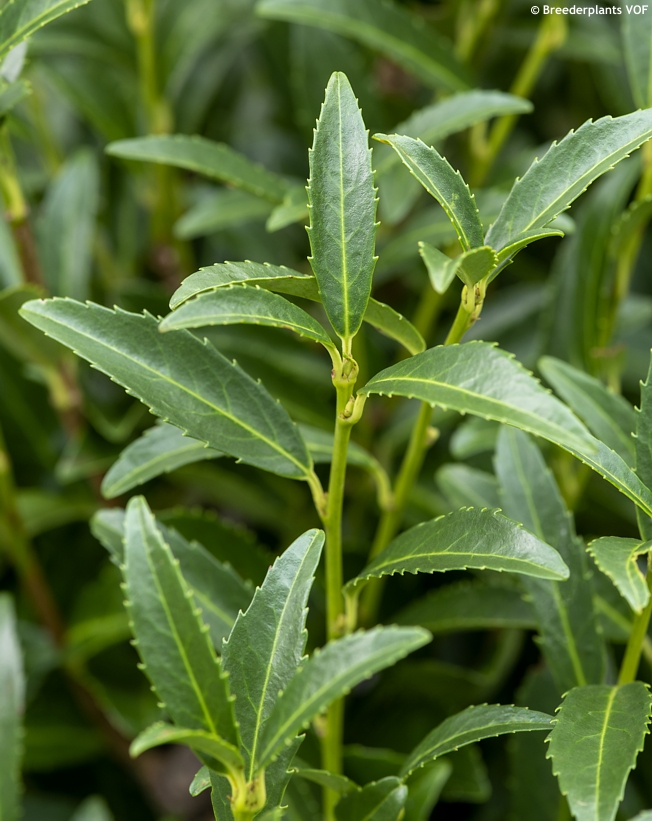
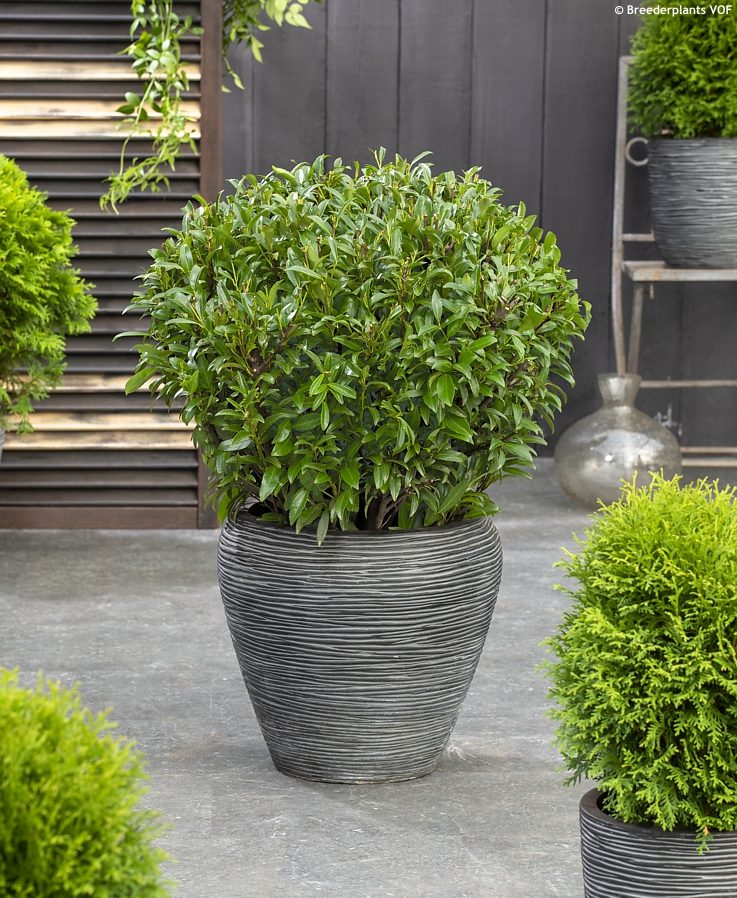
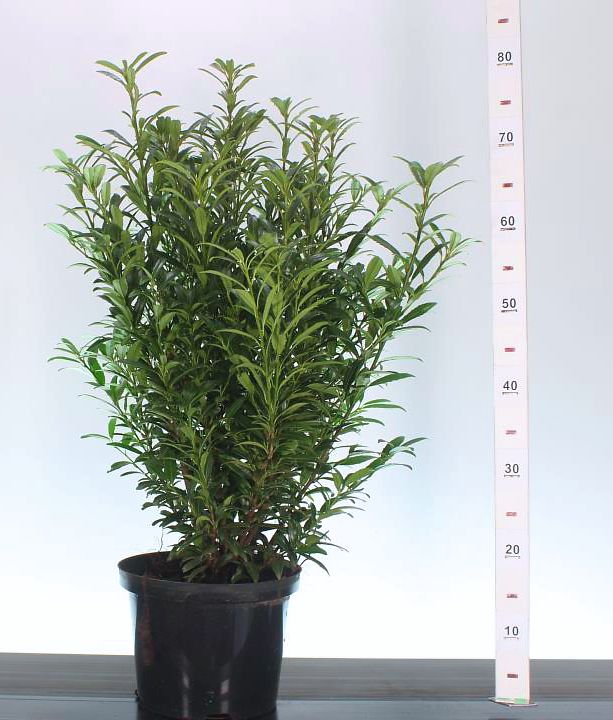
SOFIA is a dwarf cherry laurel that can easily be mistaken for a holy because of its distinctly serrated (not spiny) leaves. Hoar frost makes a picturesque sight in autumn and winter and you will want to make a photo of them every time you pass them by. They are evergreen, leathery, narrowly lance-shaped, dark green, and glossy. The plant is compact, slow growing (5-15 cm per year), densely branched, and reaches about 1.5 m in height and width in maturity. Flowers have not been observed so far. Pruning is possible in mid spring before new leaves emerge or in mid summer.
Cherry laurels require moist but well‑drained soil, ideally acidic to neutral and rich in nutrients. They do not tolerate compacted, heavy clay, muddy, or permanently waterlogged soils. They are sensitive to lime in the soil, which most commonly manifests as chlorosis – the leaves lose their green colour and the vein pattern becomes pronounced. Similar symptoms may also occur in cases of nutrient deficiency. In both situations, the application of magnesium sulphate (Epsom salt), organic fertilisers, or adjustment of soil pH towards a more acidic reaction is beneficial. They tolerate pruning of any intensity and respond particularly well to rejuvenation pruning into old wood, from which they readily regenerate. The best time for pruning is in spring after the risk of frost has passed; shaping cuts are carried out in mid‑summer. Because they retain their leaves year‑round – even in winter – and continuously transpire water, they require an adequate supply of moisture. Until a sufficiently deep root system develops, it is advisable to water them at least once a month during dry winters to prevent dehydration and subsequent leaf scorch caused by strong winter sun. To retain moisture and protect against temperature fluctuations, year‑round mulching is strongly recommended. The breeder confirms hardiness to at least -25 °C (USDA zone 5b) without any injury, however, the plant has not been tested in harsher condition yet and may take a few degrees lower.
Last update 09-09-2021; 22-12-2025
Goods are shipped all over Europe. For Russia and U.K. and for further details please read about SHIPPING OPTIONS HERE.
Are you interested in a serious discount for orders NOV-FEB? Check your options here.
THE PRICES INCLUDE VAT of 15%. For quick conversion you can use 1 CZK = approx. 0.04 EUR
- STANDARD QUALITY - Plants of this group are 1st class quality with number of branches and overall density adequate to their size and age, considering they were container grown.
- DE LUXE QUALITY - This label guarantees a luxurious quality of manually selected plants that, compared to their height and age, are exceptionally dense and beautiful.
- EXTRA - These plants are usually mature and bigger specimens with exceptional overall appearance.
- STANDARD (as described in the plant form) means a tree with a trunk of 190-210 cm and a crown at the top, unless specified differently. The commercial size for trees is their girth measured in the height of 1m from ground.
- HOBBY - These plants are of the same quality as our standard-quality plants but younger and therefore cheaper.
- SHRUB - a woody plant with branches growing bushy from the ground level.
- HALF-STANDARD or MINI-STANDARD - a small tree with shorter trunk, its size is usually specified.
- FEATHERED - These are trees with branches growing already from the base of the trunk and up along the stem.
- GRASSES and PERENNIALS - Sizes given usually read the diameter of the pot or the clump, as specified.